How to repair your damaged knee?
WHAT CAUSES KNEE PAIN AND HOW TO REPAIR YOUR DAMAGED KNEE?
Dr.K.Vijayaraghavan,MD.,FIPM(Germany)
Phoenix Pain Management Centre
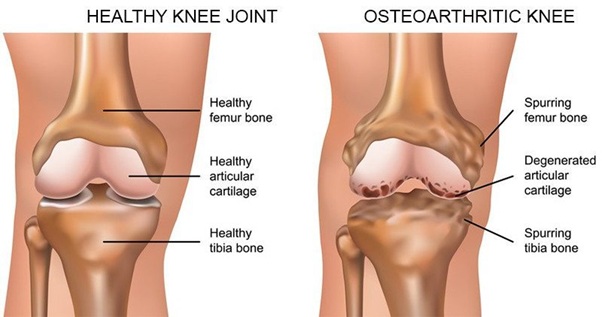
 About 1 in 5 people live with the knee pain, which is mainly due to osteoarthritis, the wear-and-tear form of arthritis. Osteoarthritis is the most common cause of disability among adults, and it frequently appears in the knee joints. Once the disease process has started, it is difficult to reverse the joint damage — which is why it’s so important to prevent knee osteoarthritis from progressing.
About 1 in 5 people live with the knee pain, which is mainly due to osteoarthritis, the wear-and-tear form of arthritis. Osteoarthritis is the most common cause of disability among adults, and it frequently appears in the knee joints. Once the disease process has started, it is difficult to reverse the joint damage — which is why it’s so important to prevent knee osteoarthritis from progressing.
The likelihood of developing knee osteoarthritis symptoms increases with each decade of your life, especially between the ages of 55 and 64, says a research.
Pain occurs when the cartilage covering the bones of the knee joint wears down. Areas where the cartilage is worn down or damaged exposes the underlying bone. The exposure of the bone allows increased stress and compression to the cartilage, and at times bone-on-bone contact during movement, which can cause pain. Because the knee is a weight-bearing joint, your activity level, and the type and duration of your activities usually have a direct impact on your symptoms. Symptoms may be worse with weight-bearing activity, such as walking while carrying a heavy object.
Symptoms of knee OA may include:
- Worsening pain during or following activity, particularly with walking, climbing up or down stairs, or moving from a sitting to standing position
- Pain or stiffness after sitting with the knee bent or straight for a prolonged period of time
- A feeling of popping, cracking, or grinding when moving the knee
- Swelling following activity
- Tenderness to touch along the knee joint
- Stiffness in knee joint especially in the morning
Osteoarthritis can be diagnosed by clinical findings and can be confirmed by X-ray and MRI.
How can it be prevented?
- Maintaining healthy weight
- Controlling your blood sugar level.
- Regular walking with proper footwear on a flat even foot path.
- Muscle strengthening exercise.
- Low impact exercises
- Managing occupational risks (Kneeling,bending,twisting,walking)
- Nutritious diet
How to treat the damaged joint?
Rest is the first line of treatment.
Ice / Heat: Applying ice or cold packs to the knee can reduce inflammation and swelling, especially after an injury. Once swelling is gone, heat may be used to help relax and loosen tissues – although ice is the primary treatment.
Using Knee Braces
Pain relievers
Weight loss: Lose weight to reduce pressure on the knees.
Knee-Injections in the Knee Joint: Potent anti-inflammatory agents can be injected inside the knee to reduce pain and inflammation. Ozone Gas can also be injected into the knee to reduce pain and inflammation. Another nonsurgical injection technique that can provide relief from knee pain is viscosupplementation. This treatment involves injecting a lubricant into the knee. The filler lubricates and adds cushioning to the joint, allowing bones to move more easily and reducing friction. It is a viable solution for mild to moderate OA.
Stem Cell / Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy: PRP therapy involves injecting platelets from the patient’s own blood to rebuild a damaged tendon or cartilage. It has been successful in not only relieving the pain, but also in jump starting the healing process. The patient’s blood is drawn and PRP cells are extracted using special PRP kits and PRP machine. The platelet-rich plasma is then injected into the damaged portion of the tendon or cartilage. It heals the joint.
Physical therapy: Physical therapies can help you recover from the injury and decrease the pain you are experiencing. They may also include low-impact stretches and exercises that can strengthen muscles in your knee, improve stability and flexibility, and reduce pressure on the joint.